Although blockchain technology has only been effectively employed in the past decade, its roots can be traced back far further. A 1976 paper on New Directions in Cryptography discussed the idea of a mutual distributed ledger, which is what the blockchain effectively acts as. That was later built upon in the 1990s with a paper entitled How to Time-Stamp a Digital Document. It would take another few decades and the combination of powerful modern computers, with the clever implementation with a cryptocurrency to make these ideas viable.
Blockchain
Where did blockchain come from
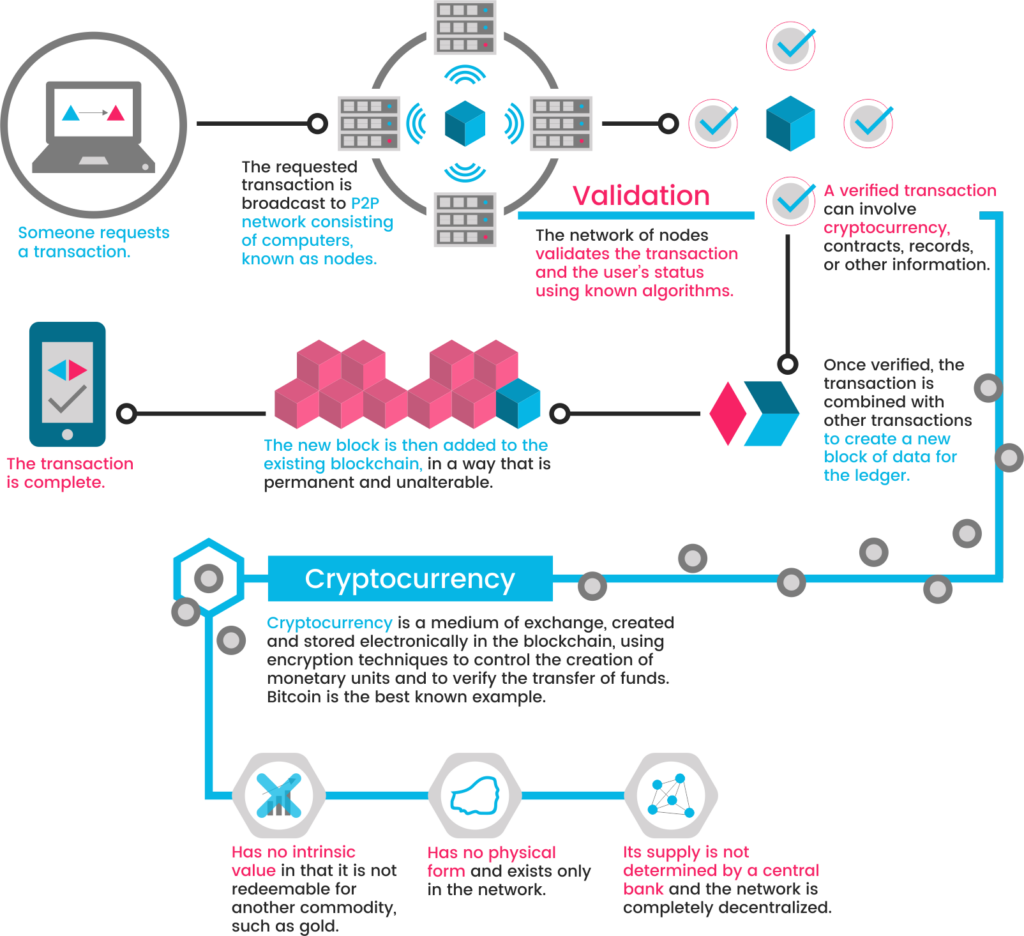
What is Blockchain
Blockchain is a type of distributed ledger where it runs on computers provided by volunteers (compensated) around the world, there is no central database to hack. The blockchain networks can be private with restricted membership similar to an intranet, or public, like the Internet, accessible to any person in the world. Public blockchains can be viewed at any time by anyone because it resides on the network. All data and transactions are verified, cleared, and stored in a block which is link to the preceding block, thereby creating a chain. Each block must refer to the preceding block to be valid. This structure permanently timestamps and stores exchanges of value, preventing anyone from altering the ledger. Blockchain is a distributed ledger representing a network consensus of every transaction that has ever occurred. Like the World Wide Web of information, it’s the World Wide Ledger of value – a distributed ledger that everyone can download and run on their personal computer.
This new digital ledger of economic transaction can be programmed to record virtually everything of value and importance to humankind;
- Birth and death certificates
- Financial accounts
- Medical data
- Marriage licenses
- Deeds an titles of ownership
- Educational degrees
- Insurance claims
- Votes
- Provenance of food
- And anything else that can be expressed in code
In fact, soon billions of smart things and devices in the physical world will be sensing, responding, communicating, buying their own electricity, sharing important data, doing everything from protecting our environment to managing our health. This Internet Of Everything needs a Ledger Of Everything. As one can see the potential of blockchain is unlimited.